Oracle Architecture

Explain Oracle Architecture?
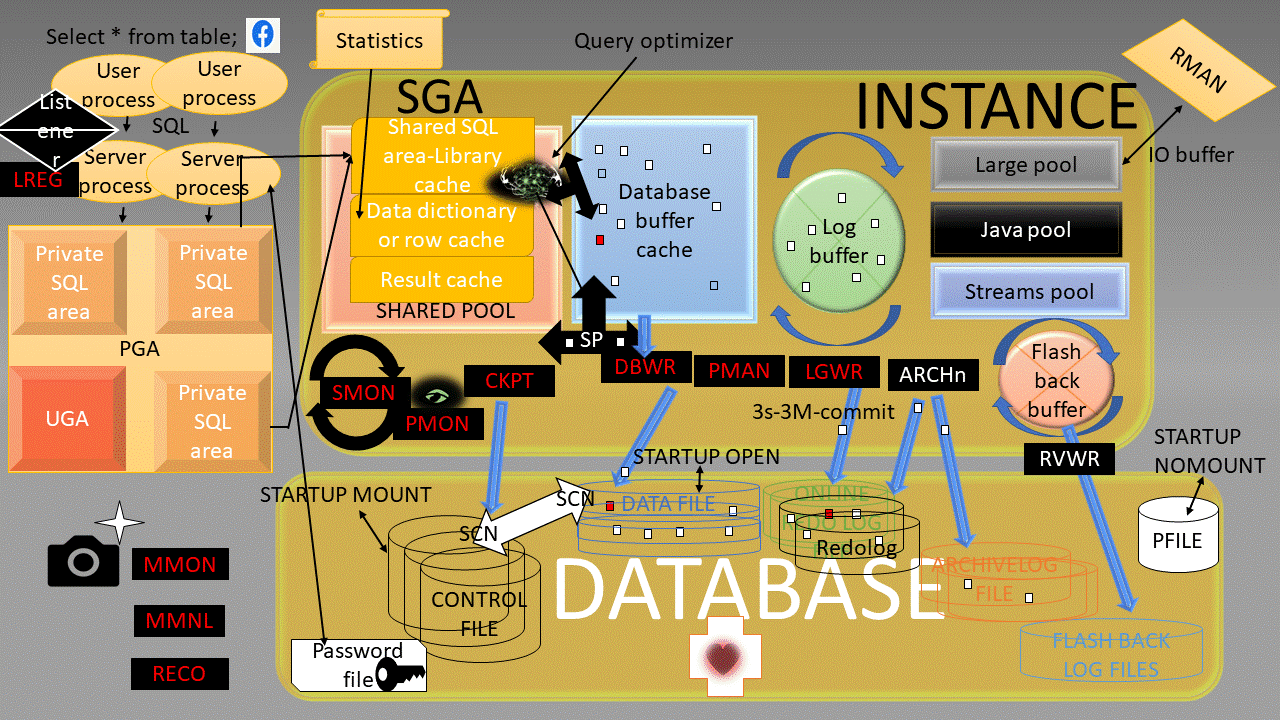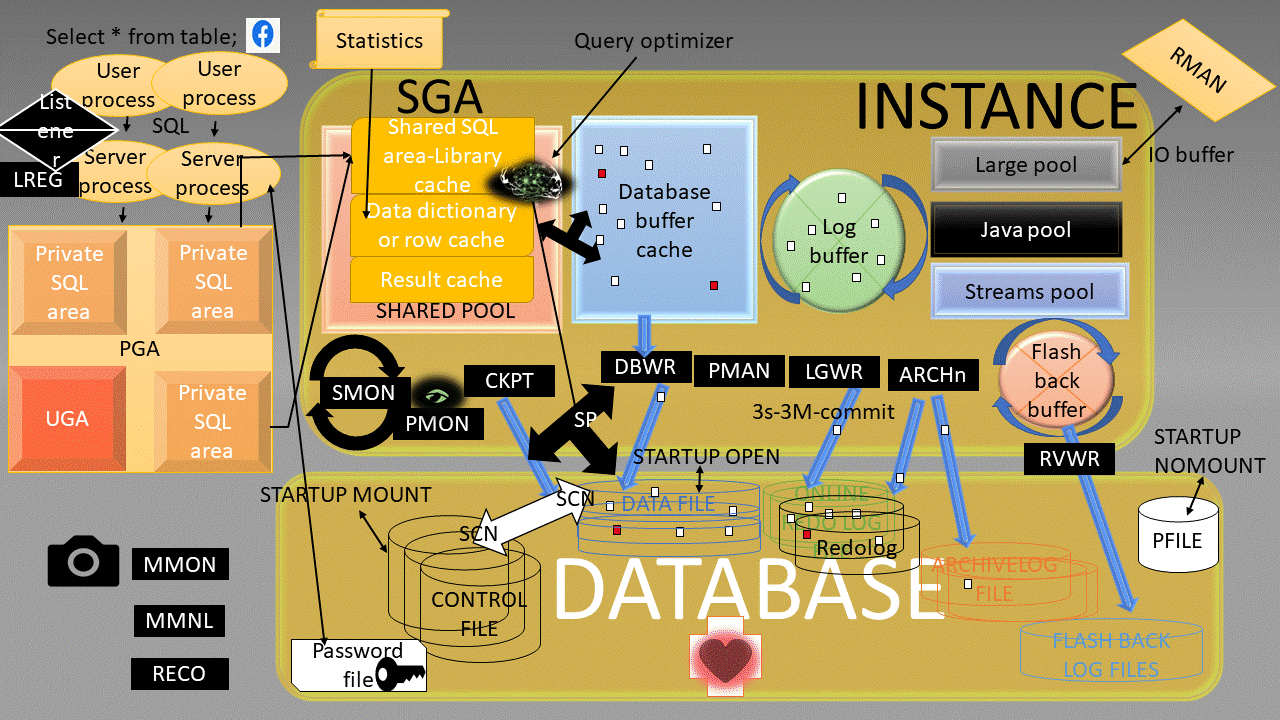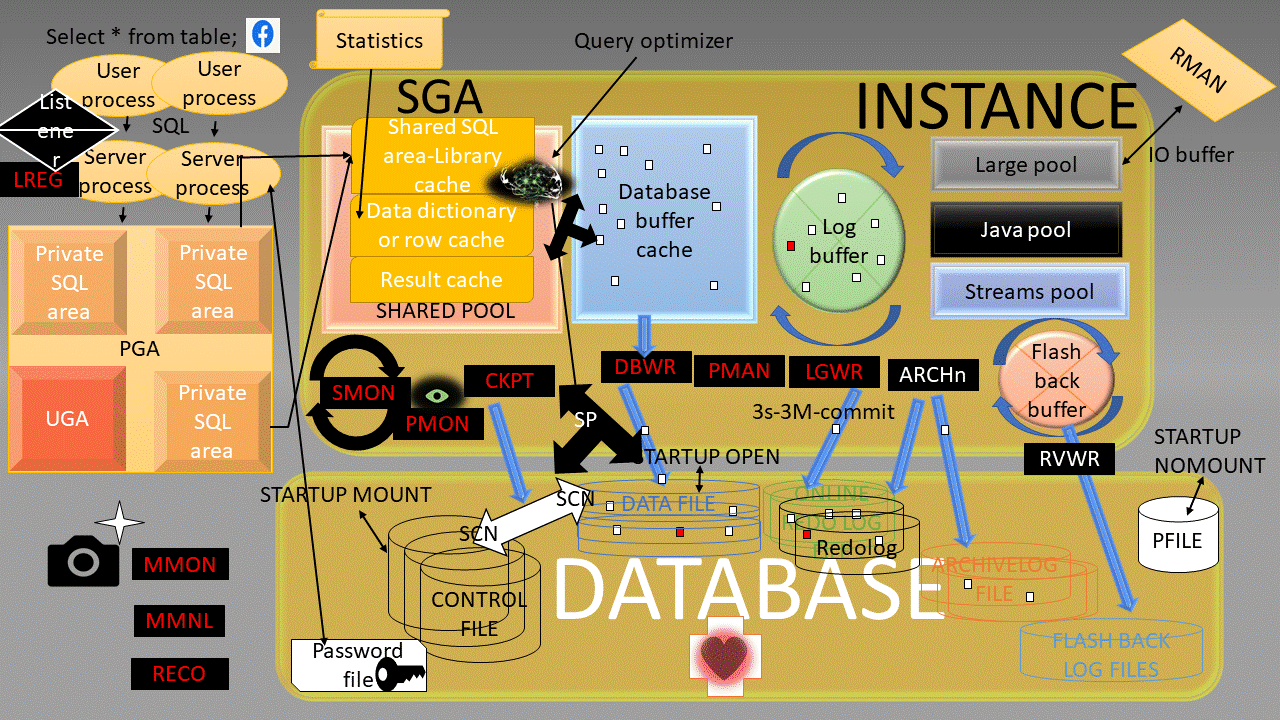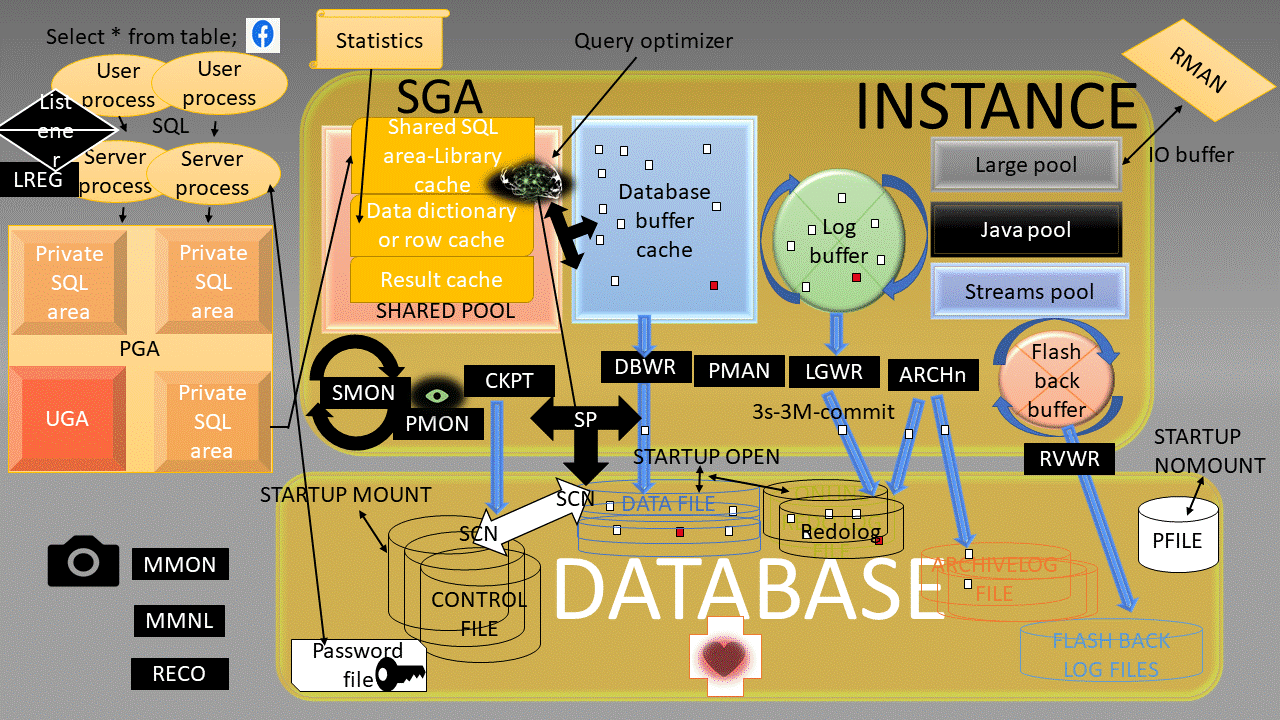
Oracle Instance:
a means to access an Oracle database,always opens one and only one database and consists of memory structures and background process.
Oracle server:
a DBMS that provides an open, comprehensive, integrated approach to information management,Consists of an Instance and a database.
Oracle database:
a collection of data that is treated as a unit,Consists of Datafiles, Control files, Redo log files. (optional param file, password file, archived log)
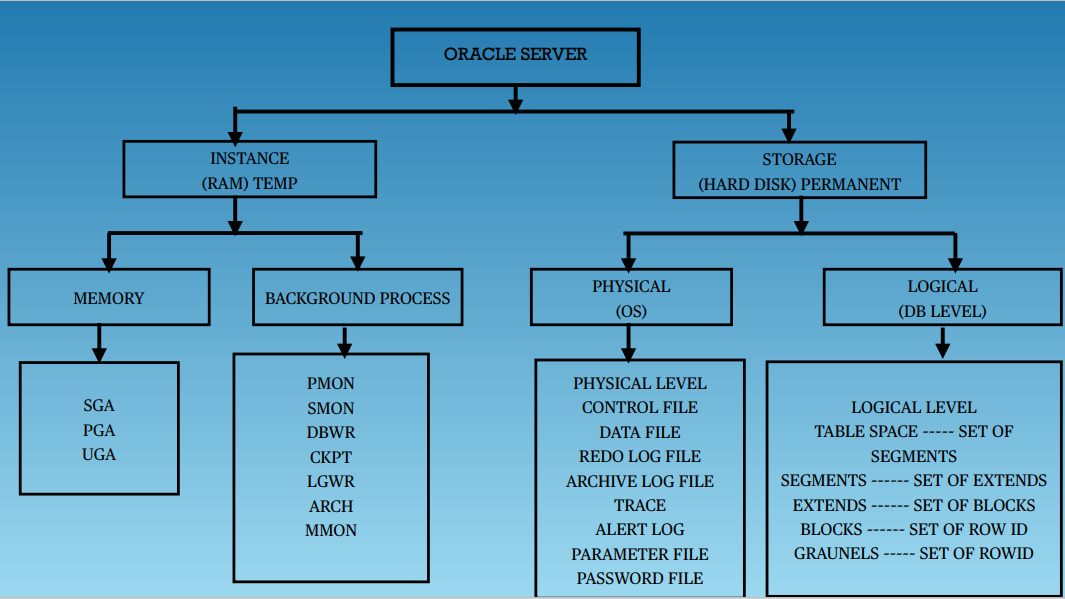


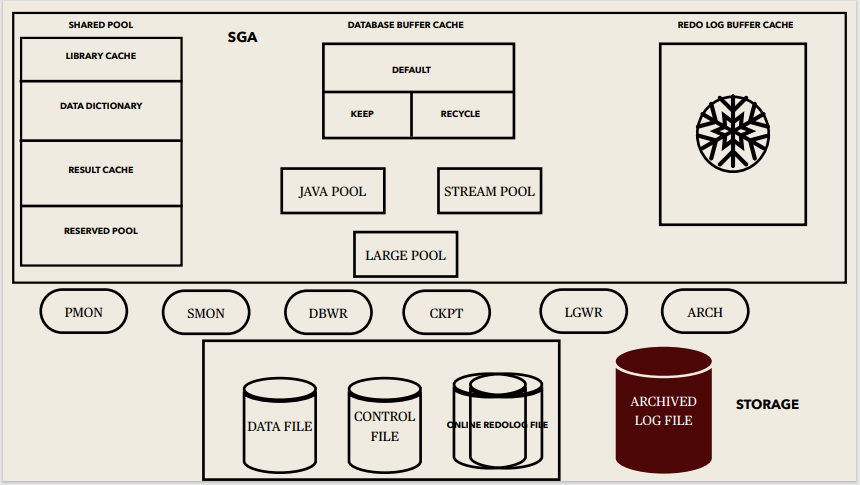
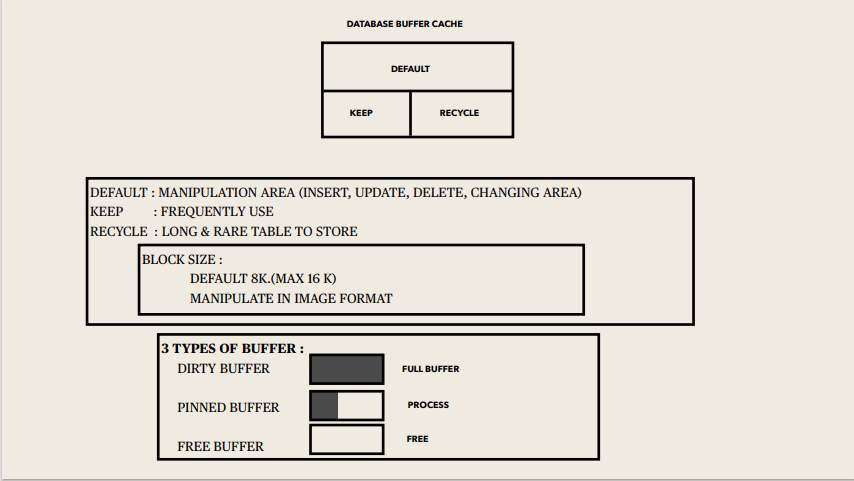
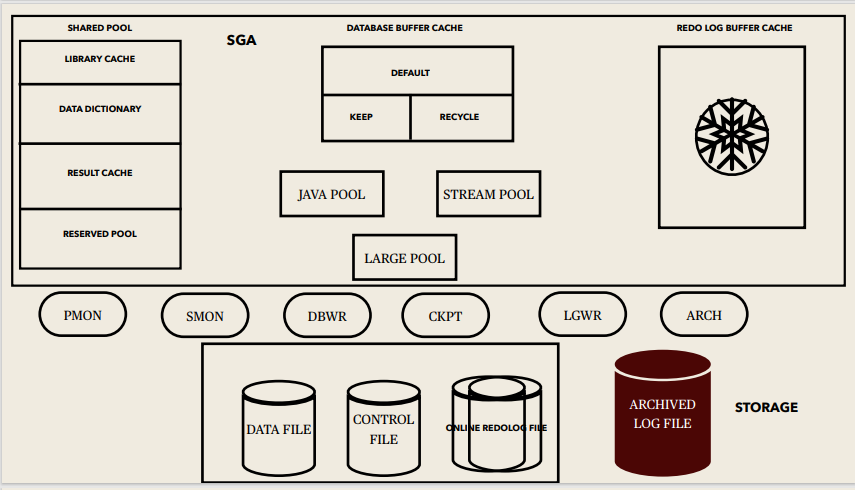
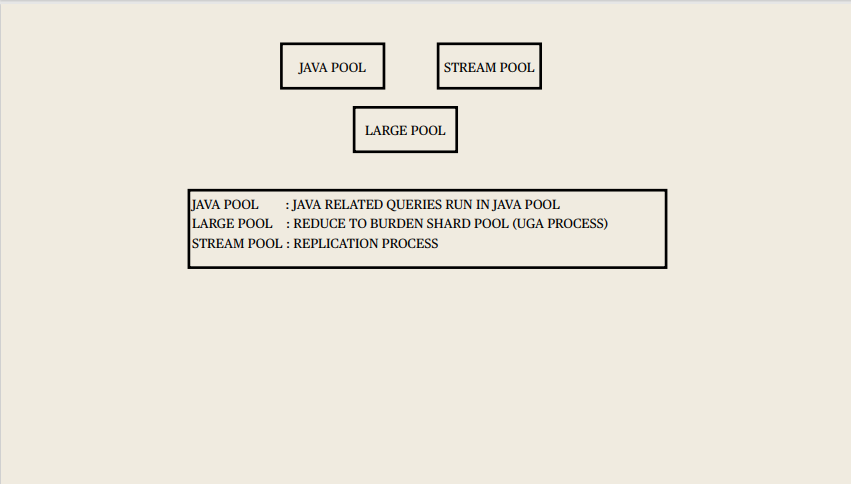
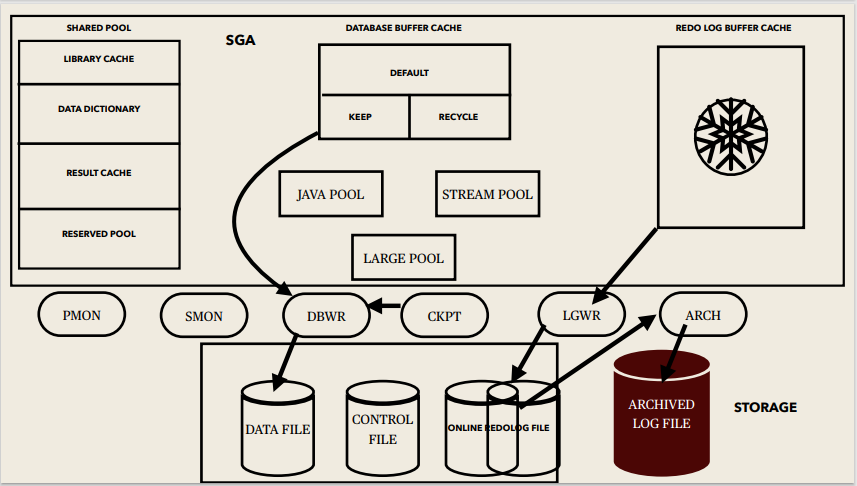
Instance memory Structures:
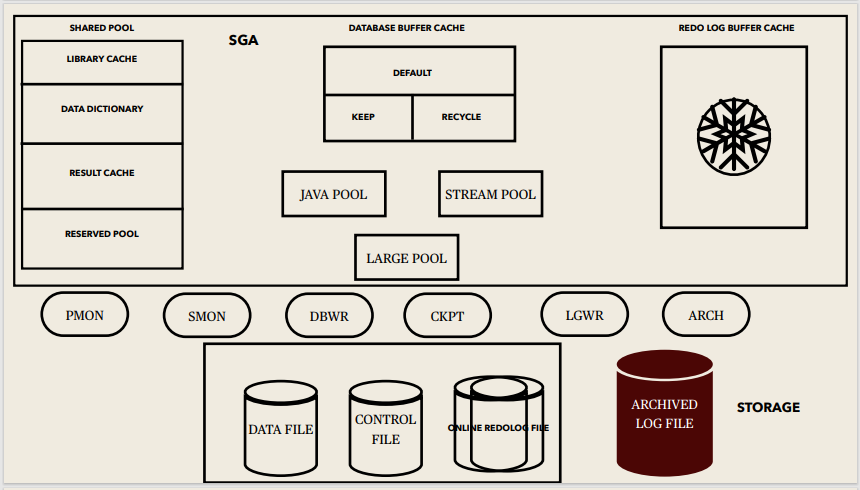
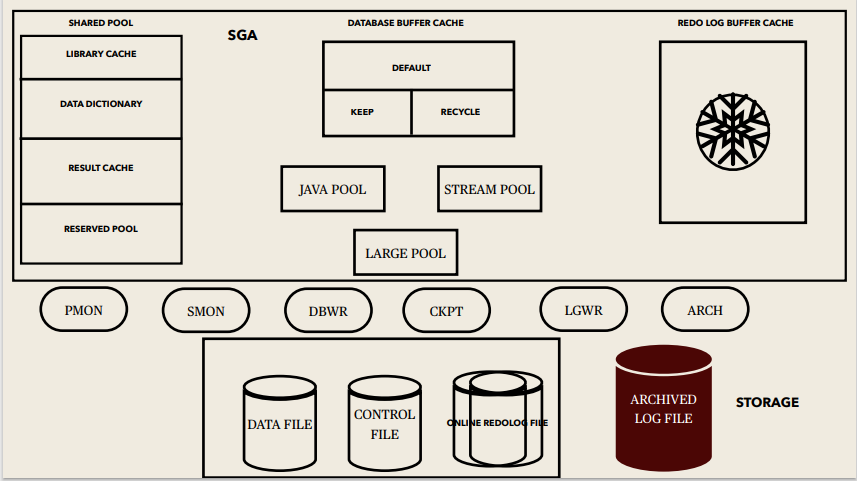
System Global Area (SGA):
SGA Memory structures:
Includes Shared Pool, Database Buffer Cache, Redo Log Buffer, Data Dictionary Cache, Database Buffer Cache, User process, Server process
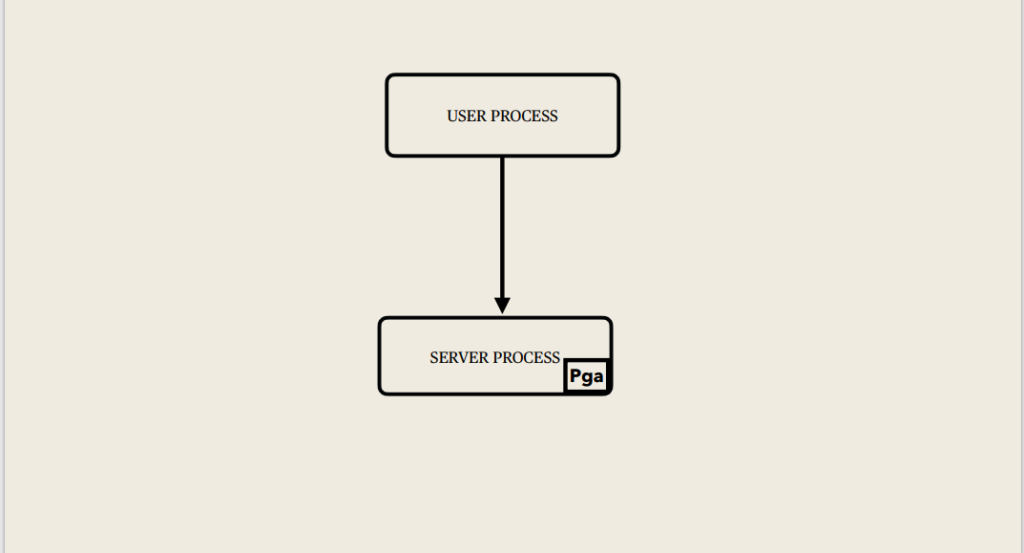
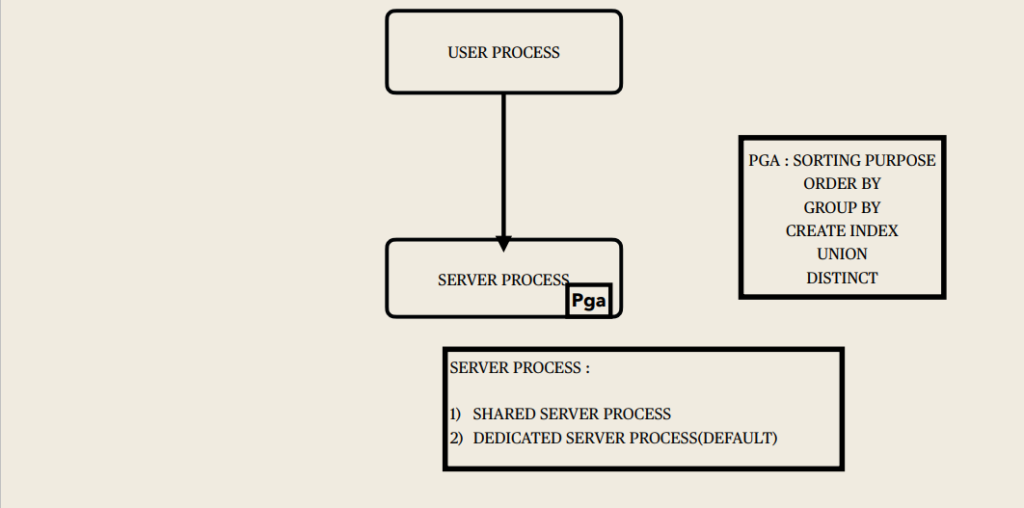
Program Global Area (PGA):
Memory area used by a single Oracle server process.
Allocated when the server process is started, deallocated when the process is terminated and used by only one process.
Used to process SQL statements and to hold logon and other session information.
Background processes:
Started when an Oracle Instance is started.
Background Processes Maintains and enforces relationships between physical and memory structures
There are two types of database processes:
1. Mandatory background processes
2. Optional background processes
Mandatory background processes:
– DBWn, PMON, CKPT, LGWR, SMON
Optional background processes:
– ARCn, LMDn, RECO, CJQ0, LMON, Snnn, Dnnn, Pnnn, LCKn, QMNn
System Monitor (SMON) Responsibilities:
- Instance recovery
Process Monitor (PMON) Cleans up after failed processes by: - Rolling back the transaction
- Releasing locks
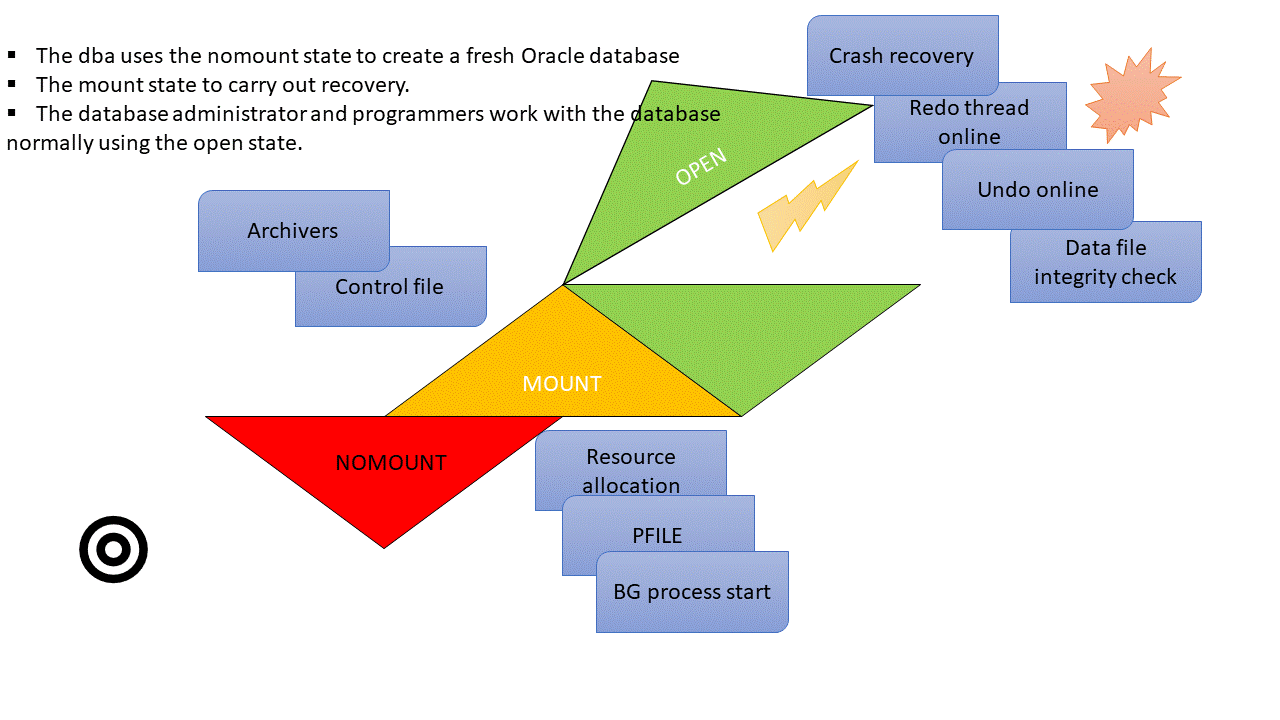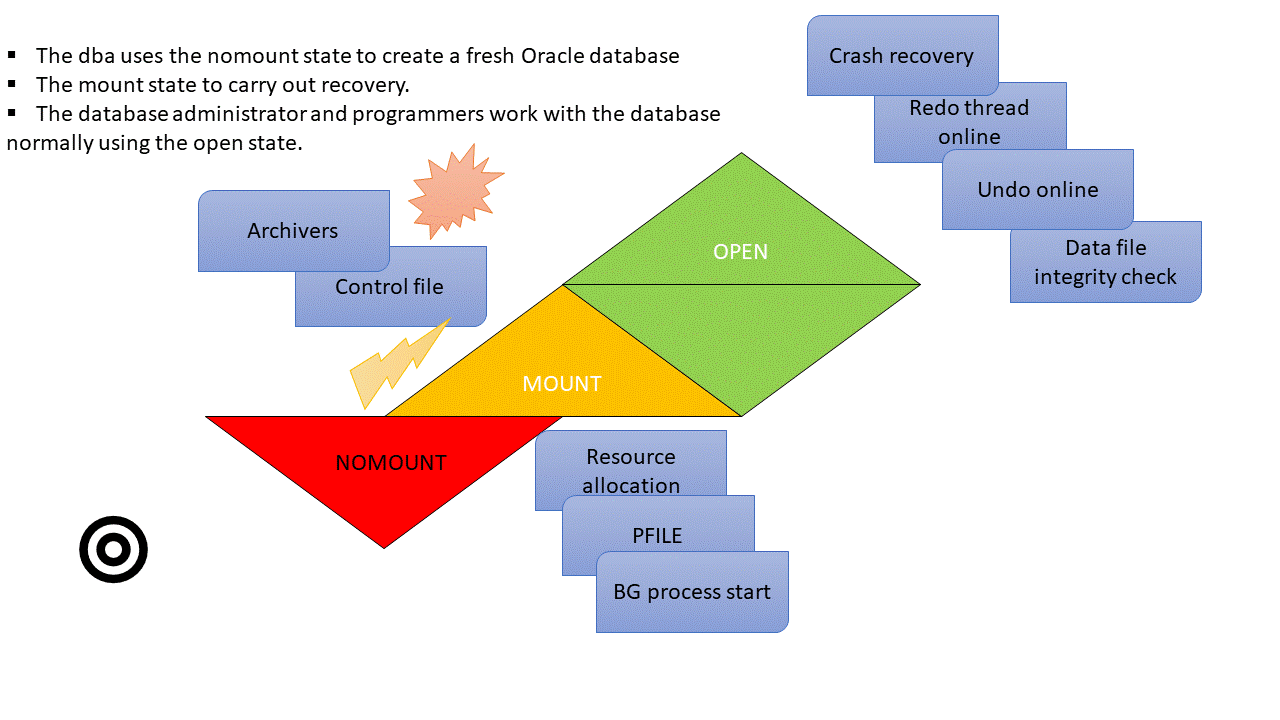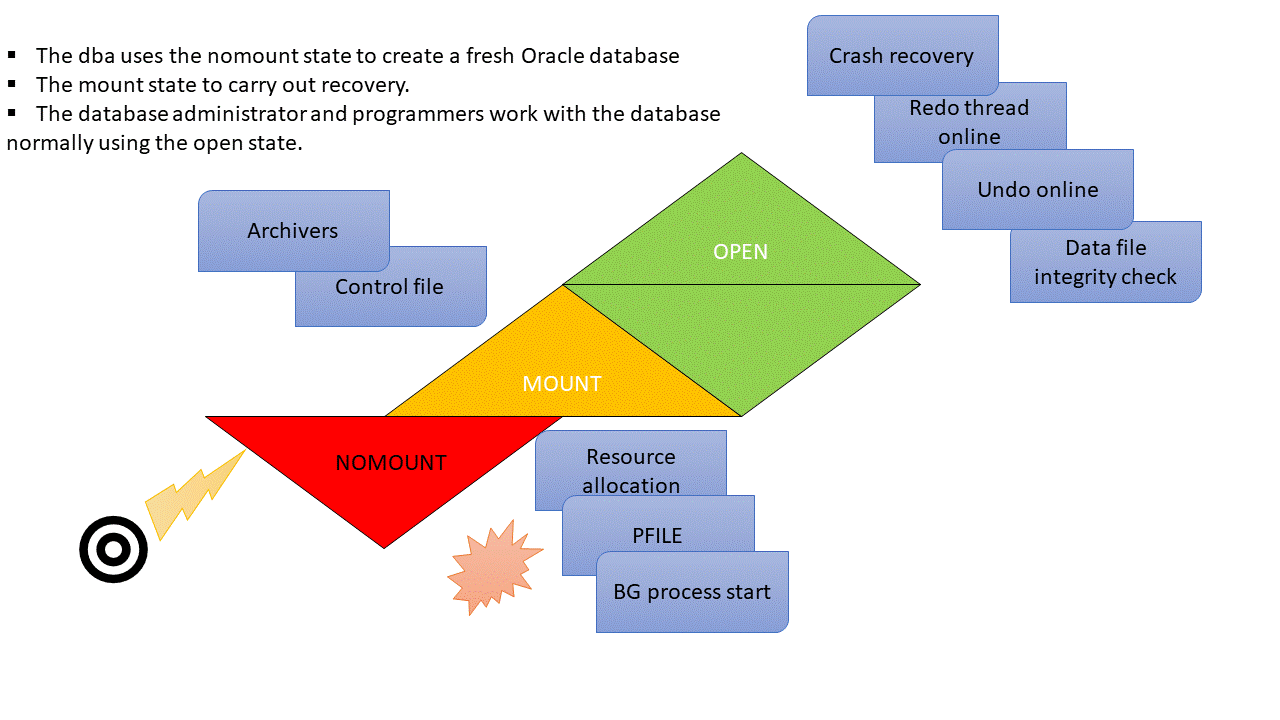
Database Startup Phases: